It is the process of discovery, evaluation and the Establishment of efficacy of identified synthetic or natural chemicals. Identification means, finding of any chemical synthesized or obtained from natural sources like microbial cells or herbal / plant extracts. Establishment of efficacy related with the findings that the new antimicrobial agent is effective against which organism, i.e. against bacteria (which strain), or fungi. Establishment of effective concentration, means determination of concentration at which the chemical effectively kills the bacterial strains and also determination of MInimum Inhibitory Concntration (MIC). So in the assesment of any new Antibiotic some properties will be established like
- The antibiotic is effetive against which microbial strain.
- What is the efficacy of new chemical (Antibiotic), and
- what is the minimum inhibitory concentration, which can show bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal activity.
Agar Diffusion Method:
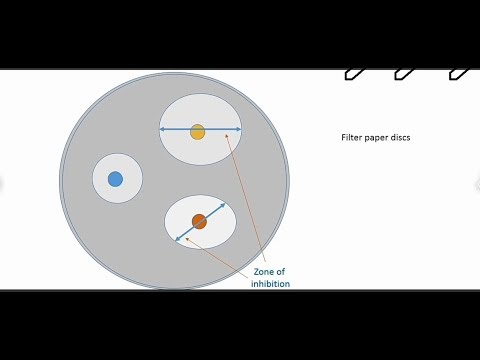
This method is most applied method for assessment of antimicrobial activity. In this method agar plates are inoculated with any microbial cells (against which the antimicrobial activity is to be tested). For this, the microbial cells are spread evenly (with the help of sterile cotton swab) on the surface of solidified nutrient agar media. Then this seeded culture media is allowed to incubate in optimized conditions to allow the growth of microbial cells. After appropriate incubation, microbial cells formed a uniform layer over the surface of nutrient agar media (This is called Lawn Culture). Then a filter paper discs are taken and wetted or impregnated with the fixed quantity and known concentration of the chemical to be tested. Then these wet paper disks are placed over the surface of culture media. Due to this the test chemical is diffused from paper disk and also diffuse into the agar media. After sometime there will be a clear area is formed around the paper discs. This area is called zone of inhibition.
Interpretation of Results
Zone of inhibition formation shows that the microbial cells are killed or destroyed by the test chemical, this indicated that the test chemical is effective against selected microbial cells. The diameter of the zone of inhibition shows the effectiveness of test chemical, as much as the diameter of zone of inhibition, as much as the test chemical is effective against selected microbial cells.Antimicrobial Gradient Test (E-test)
This method provides two types of information about any test chemical:
- Sensitivity of selected microbial cells towards any test chemical
- Information about Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of test chemical. MIC of any chemical is that concentration below which there is no antimicrobial activity.

Dilution Method:
This is most basic method for assessment of any newer or established antimicrobial compounds. In this method several dilutions of test chemical are prepared in two fold concentrations i.e. 1 µg/ml, 2 µg/ml, 4 µg/ml, 8 µg/ml, 16 µg/ml, 32 µg/ml……and so on, in nutrient growth broth medium (2 mL). (Broth is liquid medium, not solid culture medium). These dilutions are then filled in small tubes or 96 well tubes. Then a fix quantity of bacterial cell suspension is added in these tubes and allowed to grow in suitable conditions. After some time the dilutions are checked for survival of bacterial cells. For this viability indicators are used. Viability indicators are the compounds metabolized by the microbial cells and produce coloured products. So after addition of viability indicators, colour production in each tube was checked. Viability indicators are: Tetrazolium salts, Alamar blue dye (Resazurine) The tube which showed no colour production, indicate that there is no viable cell. By using this principle the minimum concentration is determined which kills the bacterial cells.